Somatic Healing 101 How Moms Can Release Stress Stored in the Body
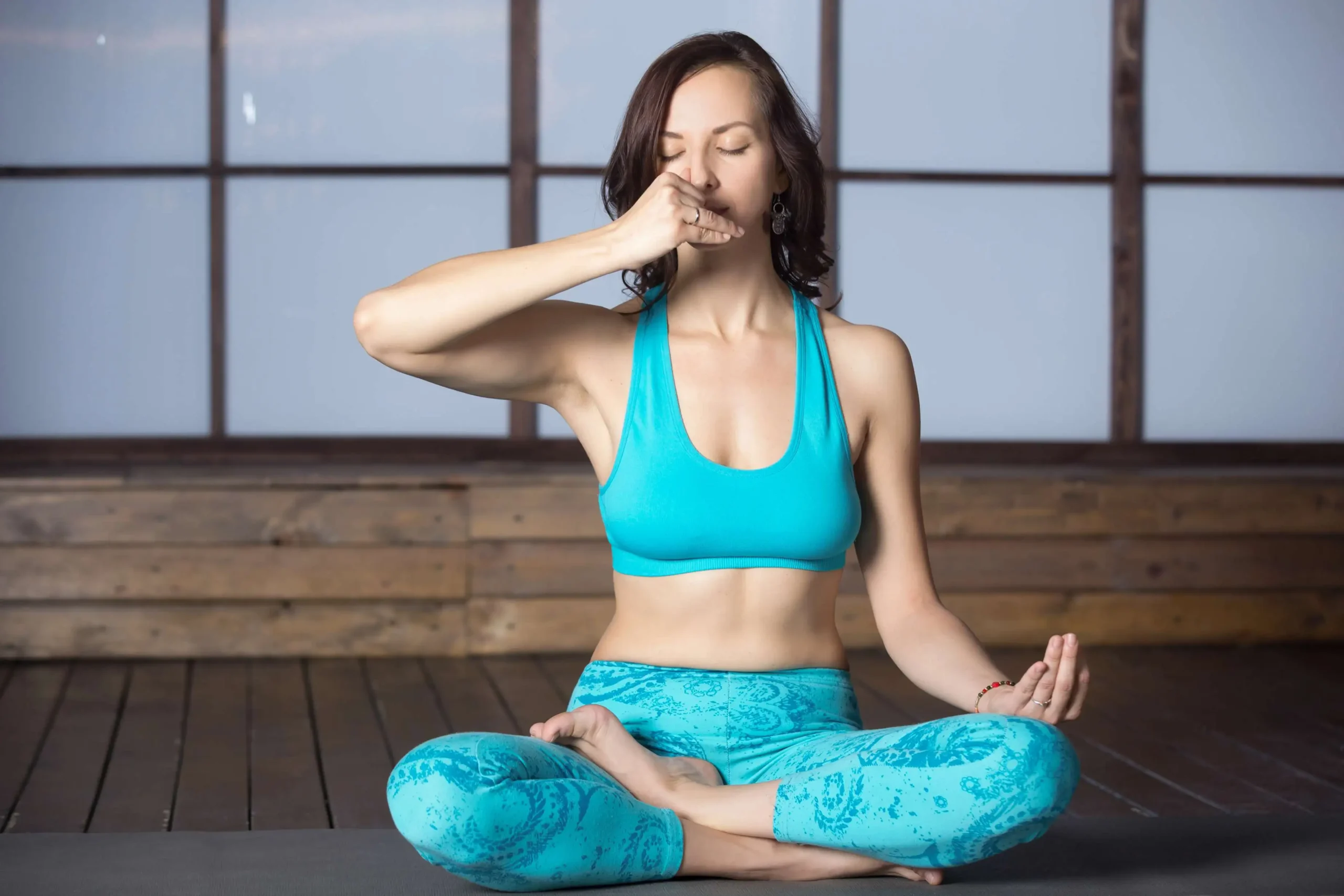
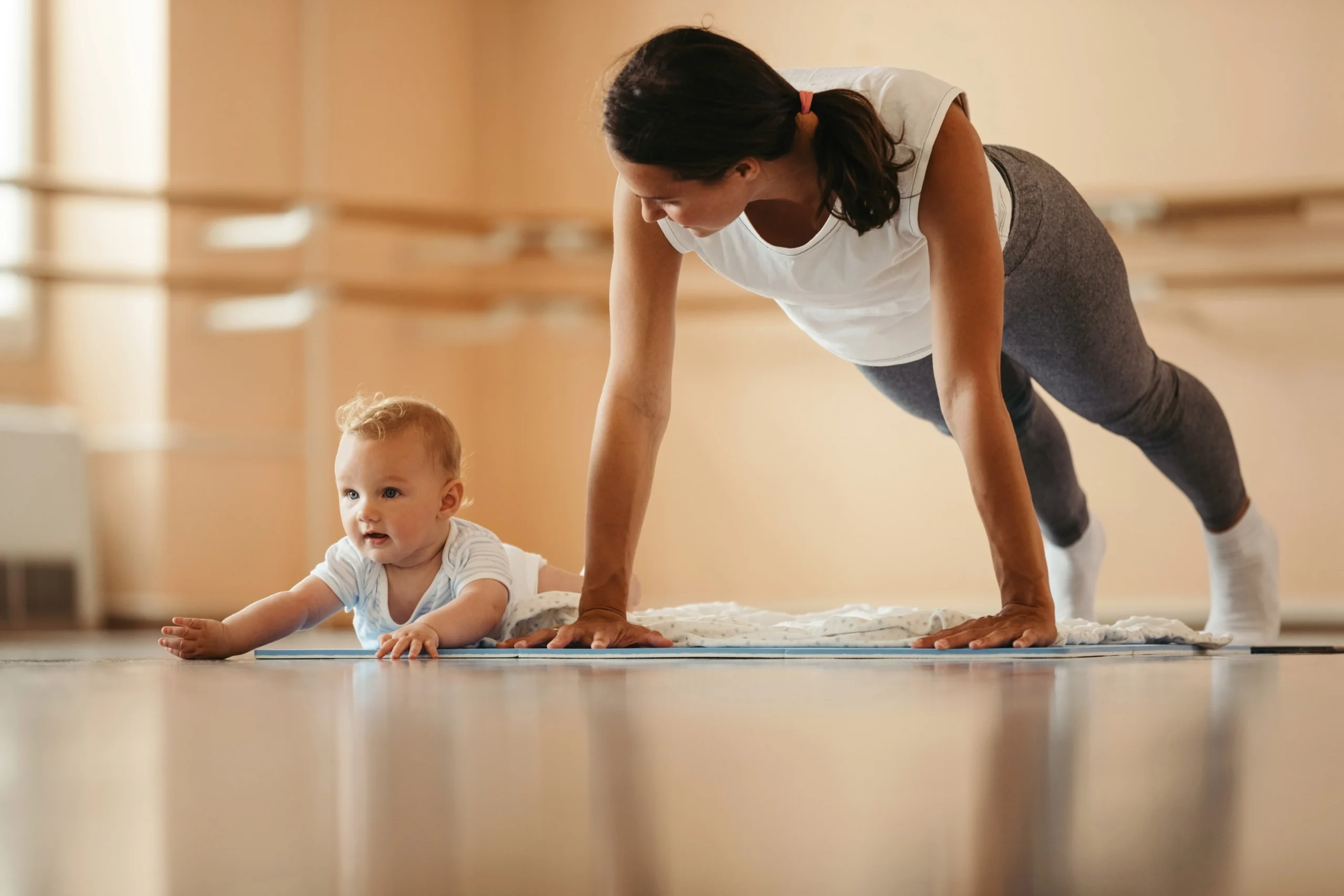
Somatic Healing 101: Why Your Body Holds Stress and How to Release It Motherhood is beautiful but let’s be honest, it’s also intense. From interrupted sleep to mental overload, many moms feel stressed even when their mind knows everything is okay. That’s because stress doesn’t just live in your thoughts it lives in your body. Welcome to somatic healing, one of the biggest wellness trends of 2026, and a powerful tool every mom should know about. What Is Somatic Healing? Somatic healing focuses on the connection between the body and the nervous system, rather than relying only on mindset work or talk therapy. The word somatic comes from the Greek word soma, meaning body. Instead of asking: “Why do I feel stressed?” Somatic wellness asks: “Where does my body feel unsafe, tense, or overloaded?” For moms, this approach is life-changing because much of our stress is stored physically, not mentally. Why Your Body Holds Stress (Especially as a mom) Your nervous system’s job is to keep you safe. When it senses danger emotional or physicality activates the fight, flight, or freeze response. As a mom, your body may interpret these as “threats”: Chronic lack of sleep Emotional labour and mental load Postpartum changes Constant multitasking Never fully “resting” Even when the moment passes, your body may stay stuck in survival mode, holding tension in places like: Jaw and neck Shoulders and upper back Hips and pelvic floor Stomach and chest This is why relaxing your mind alone doesn’t always work. Why Somatic Wellness Is a 2026 Trend In 2026, wellness is shifting from “think positive” to “feel safe in your body.” Research-backed somatic practices are gaining popularity because they: Support nervous system regulation Improve emotional resilience Reduce burnout and anxiety Help moms feel grounded faster than traditional methods For busy moms, somatic exercises work because they’re simple, quick, and body-based no extra mental effort required. Somatic Exercises for Stress Relief (Mom-Friendly & Simple) You don’t need an hour or special equipment. Try these gentle somatic practices anywhere. Physiological Sigh (Instant Calm) Best for: Overwhelm, anxiety, irritability How to do it: Inhale through your nose Take a second short sip of air Slowly exhale through the mouth Repeat 2–3 times This signals safety to your nervous system within seconds. Body Scanning for Nervous System Health Best for: Feeling disconnected or numb How to do it: Close your eyes Slowly scan your body from head to toe Notice sensations without judgment Gently breathe into tense areas Awareness alone helps release stored stress. Gentle Shaking (Somatic Release) Best for: Built-up tension and fatigue How to do it: Stand and lightly shake your arms, legs, and shoulders Breathe freely Continue for 30–60 seconds This mimics how animals release stress naturally. Grounding Through Touch Best for: Emotional regulation How to do it: Place one hand on your chest and one on your belly Apply gentle pressure Breathe slowly for 1–2 minutes This is especially helpful for overstimulated moms. Somatic Healing for Moms: Why It Works Unlike forcing calm, somatic healing: Works with your body, not against it Helps release stress you didn’t know you were holding Builds long-term nervous system resilience Fits into real mom life You don’t need to be perfectly calm you just need to feel safe enough. How to Start a Somatic Wellness Routine (Even with Kids Around) Start with 1–2 minutes a day Pair exercises with daily habits (after brushing teeth, before bed) Choose feeling better, not doing it “right” Remember: consistency beats intensity Your body has been protecting you it just needs permission to rest. Final Thoughts: Healing Doesn’t Have to Be Mental As moms, we often push through stress instead of releasing it. Somatic healing reminds us that our bodies are wise and when we listen, real healing happens. In 2026 and beyond, wellness isn’t about doing more. It’s about coming back into your body. Your nervous system deserves that care. 💛 FAQs Loved the Post? Share It!
Somatic Healing 101 How Moms Can Release Stress Stored in the Body Read More »